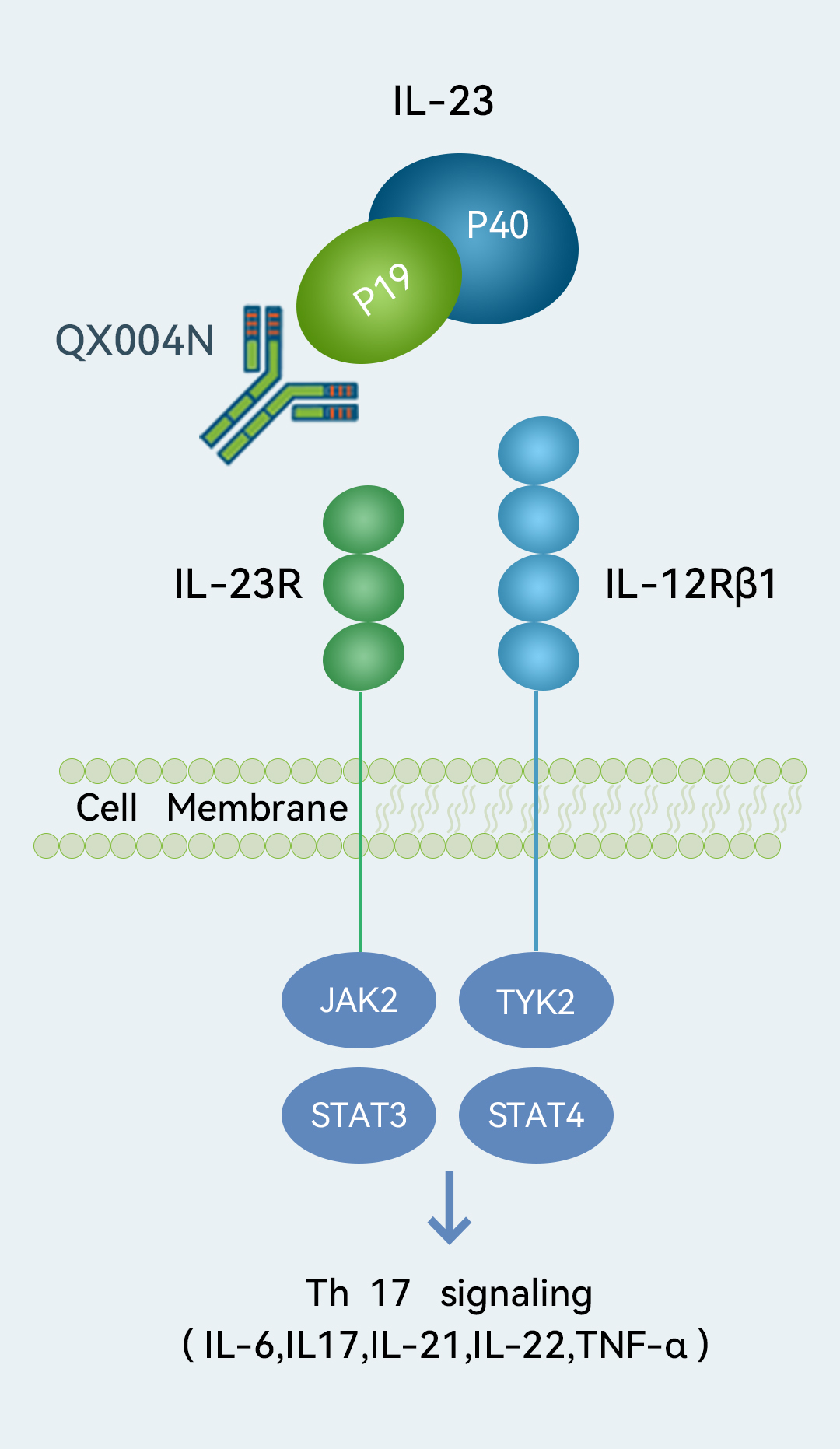
Target
Target- IL-23p19
 Generic Name
Generic Name- Recombinant humanized anti IL-23 monoclonal antibody injection
 Potential Indication
Potential Indication- Ps CD
We are developing QX004N, an IL-23p19 inhibitor, for Ps and CD. IL-23p19 has emerged as a key target associated with superior efficacy for Ps patients with more severe symptoms or inadequate response to existing treatments. QX004N showed a good safety profile based on preliminary results from our Phase Ia clinical trial. It also demonstrated a good safety profile and potency comparable to risankizumab, an FDA-approved IL-23 inhibitor for moderate-to-severe plaque Ps, in our preclinical studies. As of the Latest Practicable Date, we had commenced a Phase Ia and a Phase Ib clinical trial in China to evaluate QX004N for the treatment of Ps and expect to complete these trials in the second quarter of 2023 and the first half of 2024, respectively. We plan to initiate a Phase II clinical trial of QX004N for the treatment of Ps in China in the fourth quarter of 2023. We also commenced a Phase Ia clinical trial for the treatment of CD in China in February 2023.
For the competitive landscape of Ps drugs in China, see QX001S above. According to Frost Sullivan, the prevalence of CD in China was 160,500 in 2021, and is estimated to reach 281,400 in 2030. The significantly overlapping UC/CD drug market in China was US$885.1 million in 2021, and is estimated to reach US$5,281.9 million in 2030, at a CAGR of 22.0%. As of the March 2023, there were 11 biologic drugs for CD approved in China, including 9 TNF-α inhibitors (including infliximab, three infliximab biosimilars and five adalimumab biosimilars), 1 integrin α4/integrin β7 inhibitor and 1 IL-12/IL-23 inhibitor, namely, ustekinumab. The TNF-α inhibitors, integrin α4/integrin β7 inhibitors and IL-12/IL-23 inhibitors are expected to continue to be mainstream biologic treatments for CD in the near future.